Varicherosis is a systemic disease that can affect vessels in any part of the body. Its essence is the dysfunction of the valves that control the direction of the blood flow. For this reason, there is an accumulation of excessive volume of fluid in the veins, under the influence of which the walls extend and lose their elasticity.
Most of the time, medical publications focus on symptoms and the treatment of varicose veins in the legs, as this variety of disease is considered the most common: according to statistics, more than 80% of all cases of varicose veins are precisely in the lower limbs. However, despite this, for most patients, the diagnosis of varicose veins is a surprise and its detection occurs in the later stages. All of this indicates people's insufficient awareness of the dangers that varicose veins carry.
Characteristics, causes and mechanism of the development of varicose veins
The main feature of leg varicose veins is their vastness. The changes are subject to superficial veins and deeply running in a large length. As there is a very large and long load on the feet, the valves in the circulatory system can begin to weaken in childhood. Therefore, the detection of varicose veins in the legs usually occurs in young people and girls.
These are the lower ends that are characterized by a phenomenon as hidden varicose veins: against the background of changes pronounced in the veins and unpleasant symptoms, there are no visible signs of the disease. Therefore, in about one third of all cases, the disease is detected in advanced stages.
To perform effective treatment of varicose veins in the legs, the doctor will have to find out the causes of their occurrence. As even when using radical methods in 80% of patients, there is a relapse of varicose veins, special attention should be given to reduce the effect on the processes of factors that cause varicose veins. These include:
- The hereditary predisposition is a truly uncontrolled factor, which, however, can be contained by standard preventive measures;
- Physical influences - an increase in leg load (longtime and sitting, the habit of crossing the legs, overweight, weight lifting);
- Physiological effects - hormonal changes and hormonal drugs (usually contraceptive), metabolic disorders, lack of physical activity;
- Pathological causes are chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys, injuries and systematic cable of soft tissues from the lower extremities, tumors, squeezing the veins in the abdominal cavity.
Depending on the location of the veins, doctors distinguish various types of varicose veins:
- Surface. It is expressed by the appearance of a blue or red grid in the legs, which first resembles a web, and then the plexus of very thick winding lines.
- Deep. It is expressed by a defeat that is not visible during the external examination of the vascular plexus. Pain in the veins of the lower extremities with varicose expansion of this type is more intense and greater risk of complications.
- Combined when the deep and superficial veins are subjected to change.
The establishment of the causes of varicose veins and their elimination are in close relationship. First of all, it is important to exclude factors that have the largest negative impact on the state of the veins.
By diagnosing venous changes, it is important to differentiate them with other diseases. For example, varicose veins under the knee look equal to the Becker cyst and are accompanied by similar symptoms.
Stages
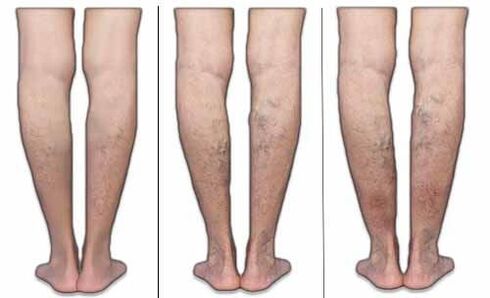
The appearance of the first signs of varicose veins in the legs occurs in progressive stages, when venous valves perform their functions by less than 50%. In the first or zero stage of varicose veins, which is known as "compensation stage", there is no discomfort, as well as visible changes. The detection of the early stage of the varicose veins in the legs occurs with careful examination of the members by a phlebologist.
In the second stage of varicose veins, which is known as "subcompensation", changes are expressed very well:
- Large vein contours are visible under the skin, but may not project above the surface of the skin;
- On the surface of the skin on the hips and under the knees, a grade pattern of thin varicose veins of blue or red capillaries is clearly visible;
- At night the legs get swollen;
- At night, the calf muscles are tight.
This stage of varicose veins of the lower extremities is distinguished by increasing symptoms, which weakens after rest.
In the final phase of varicose veins, decompensation occurs: the body cannot replenish the needs of tissues in oxygen, and the veins valves at 90% lose their functions. The condition of the limbs worsening due to insufficient blood supply. This stage of varicose veins is characterized by a decrease in tissue skills for regeneration. The abundance of complications worsens the patient's overall condition. Symptoms in the final stage of the varicose veins are constantly preserved.
Symptoms
The most common and early symptom of varicose veins is leg pain until the end of the business day. It appears with a change in deep and surface vessels and is a sign of blood supply insufficiently good for soft tissues. In some cases, pain is the only symptom of varicose veins from the deep veins of the lower extremities. With a change in surface vessels, the appearance of varicose veins in the legs, which usually creates only aesthetic inconvenience, signals the development of the disease.
The nature of pain with varicose veins at different stages of disease development may differ:
- In the early stages, there is a slight discomfort that resembles the common fatigue;
- With progression to the second stage, a burning sensation appears in the legs of varicose veins, which is usually located under the knee;
- Pulling the pain with varicose veins of the lower ends is accompanied by 2 and 3 stages of the disease, along with this, can occur cramps of the calf muscle;
- The acute pain that caused chromium occurs in the final stages of the disease.
In addition to the obvious physical discomfort, the disease is accompanied by external changes. Most patients complain that their legs scratch - with varicose veins, this is considered a normal phenomenon that indicates ischemic processes. A thin varicose veins, which practically does not bother in the early stages, over time projected stronger, becoming a thick interconnection of thickened vessels. Any physical activity, including cough, sneezing or long walks, can lead to an increased and sometimes veins. The blood is shed under the skin, forming bruises.
The presence of bruises on the legs with varicose veins indicates a stable progression of the disease, excessive stretching and vein thinning.
The appearance of red spots on the legs with varicose veins, skin peeling, thinning and exposure to lesions indicates atrophic processes that are characteristic of the final stages of the disease. The complications are indicated by the redness of the leg, which is accompanied by acute pain and lameness. This symptom is characteristic of flexes and thrombophlebitis. If the patient is blackened by the leg, this indicates a serious vein block and the beginning of necrotic processes.
Diagnosis
The ease of diagnosis of varicose veins in the legs is exaggerated, as the vessels do not always reach the surface. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor must perform an external exam and perform a series of instrumental research:
- Examination or duplex ultrasound in the lower limb - for varicose veins, it is first used to determine the degree of stretching of the vascular walls, the nature of blood flow and detect blood clots;
- Contrast limbs radiography - the functional examination pattern for the lower extremities' varicose veins, which allows to determine blood vessel forgness;
- Magnetic resonance imaging is the modern diagnostic pattern of varicose veins at the lower extremities, which allows to evaluate the functionality of venous valves, identify mole -tissue ischemia outbreaks, detect blood clots and other pathological changes that have emerged against the background of varickers.
To clarify the complete image of the disease, laboratory studies are prescribed: a coagulogram to assess the risk of thrombosis, a general blood and biochemical examination.
Treatment Characteristics
The treatment of varicose veins in the legs is involved in a phlebologist. After determining the degree of pathological changes, the doctor selects the most effective, in his opinion, therapy methods. Unfortunately, it will not work to get rid of the varicose veins in the legs forever, since the disease is systematic and even modern treatment methods provide a long but not 100% stable result.
According to statistics, even after the use of radical methods for the treatment of lower extremity varicose veins in 80% of patients, relapses occurs for 5 years.
In the early stages of varicose veins in the legs, treatment is preferably conservative. Its base is the use of local and systemic medicines:
- Anticoagulants that reduce blood viscosity and improve tissue nutrition;
- Anti -Saggers who reduce the risk of thrombosis and improve tissue trophies;
- Venotonic to avoid greater vein stretching, reduce inflammatory processes and swelling.
With discomfort pronounced for varicose veins in the legs, the NSAIDs are prescribed. Preparations of this group help reduce pain, prevent the development of complications.
What to do if the legs of varicose veins do not allow to sleep, do family things and make it nervous? It is worth trying ointments or gels with a cooling effect. They will not affect the veins and will not help deal with the disease, but will quickly relieve the symptom.
In addition to conservative therapy, doctors often use complex treatment methods of the lower ends, when minimally invasive and surgical operations are used simultaneously with medical effects. This scheme is used for intense symptoms and extensive dissemination of venous networks. What is measuring to take and what to do if the varicose veins in the legs begin to progressively progress, a phlebologist decides. At the same time, it takes into account all aspects of disease development, the individual characteristics of the body and health problems, which can become against -indications for certain procedures.
Which methods are used to eliminate pathological vessels:
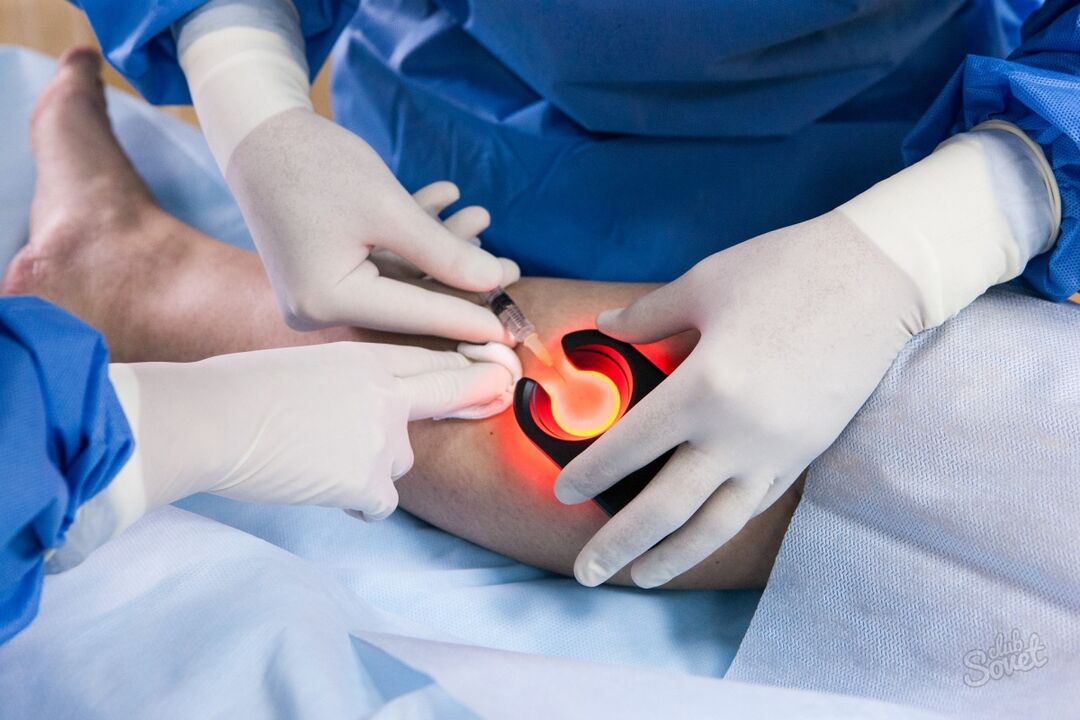
- Laser coagulation. It is used if varicose veins do not change to 2 and 3 stages, ie in the presence of small "stars" on the surface of the skin. The method is painless and effective, but expensive. There is no 100% cure guarantee, as the elimination of visible vessels occurs, while the causes of the disease are preserved. Apply to the early stages to eliminate cosmetic defects.
- Sclerotherapy. In thin and medium thicknesses, the vessels are introduced by a sclerosis, which seals the lumen of the veins, excluding -the blood flow system. The procedure is practically painless and relatively cheap, but has many against -indications. It is used in 1. 2 and sometimes 3 stages.
- Flebecctomy is a classic excision of pathological veins through perforations or cuts on the skin. This method eliminates surface varicose veins in the hips and legs. After surgery, visible scars remain, but the operation is the only effective with advanced varicose veins.
Surgical or minimally invasive intervention does not mean to complete if you get rid of the varicose veins. The patient will have to regularly visit a phlebologist, take medications to keep the vein tone and use compression linen.

Against -indications
Experts attribute against the varicose veins in the legs, any actions that may cause additional stagnation in the vessels of the lower extremities. These include:
- long stay in static poses;
- weight lifting;
- sitting with folding or crossing the legs.
In addition, patients should avoid taking alcohol, which helps increase blood viscosity and weaken blood vessel walls. Smoking can negatively affect the course of the disease. Therefore, after making a diagnosis, it is necessary to abandon bad habits.
Complications
Thrombosis and inflammatory processes on the vein walls, mentioned earlier, are far from the only thing that varicose veins in the legs are dangerous to the patient in terms of complications. Due to circulatory disorders, not only blood vessels, but also soft tissues suffer, therefore, among the consequences of varicose veins in the legs, problems with muscles and skin are mentioned:
- dermatitis, accompanied by itching, skin ulceration, itching;
- eczema, accompanied by the crack of the skin;
- Necrotic changes in the skin until gangrene formation;
- trophic ulcers;
- muscular atrophy.
Frequently, with disease progression and excessive stretching of blood vessel walls, the patient risks finding bleeding of the varicose veins of the lower extremities. It can be closed when the blood accumulates in the muscles and under the skin and forms bruises or open. The second option is full of a large blood and the arrival of a coma, especially if the patient takes anti -agents and anticoagulants.
This complication of varicose veins from the lower extremities can lead not only to injury but also to a small physical effort, for example, cough or clear movement.
The most dangerous complications of lower limb varicose veins are pulmonary artery thromboembolism and myocardial infarction. They occur due to breaking the blood clot in the femoral artery and its migration according to the blood flow system in the coronary and lung vessels. Mortality in such processes is extremely high, so it is important that the patient always follows the well -urgently to be difficult to breathe and opaque chest pain.


















